《计算机系统要素》Day02 布尔运算
本章最终将构建具有完整功能的算术逻辑单元 ALU
Day2
第二章 布尔运算
本章最终将构建具有完整功能的算术逻辑单元 ALU
所有正整数的编码首位都是0
所有负整数的编码首位都是1
补码:正整数按位取反再加1
加法器
-
半加器
对两个二进制位进行相加,结果的LSB位称为sum,MSB位称为carry
-
半加器的实现
sum位(本位):ab异或
carry位(进位):a*b
- 可以说是非常简单了
-
-
全加器
全加器除了加数a,b外,还接受一个进位c输入
-
全加器的实现
sum位: 半加a,b,半加c的sum位
carry位:两次carry位的求和

-
-
加法器
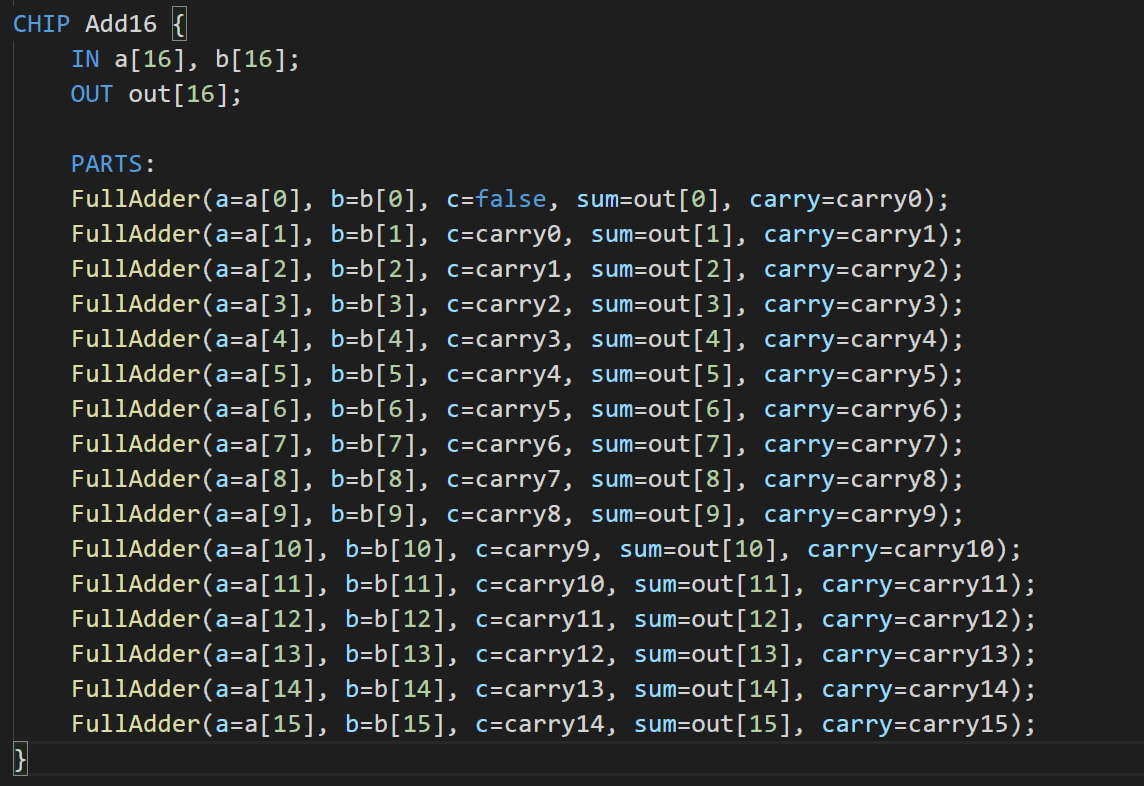
本书要求设计16位加法器,实现思路很简单,全加器一次执行本位两数加前一位进位即可。
由于有大量重复代码,所以写了一小段脚本生成代码
for i in range(16): print 'FullAdder(a=a[%d], b=b[%d], c=carry%d, sum=out[%d], carry=carry%d);' %(i,i,i-1,i,i)生成的代码稍作修改:
-
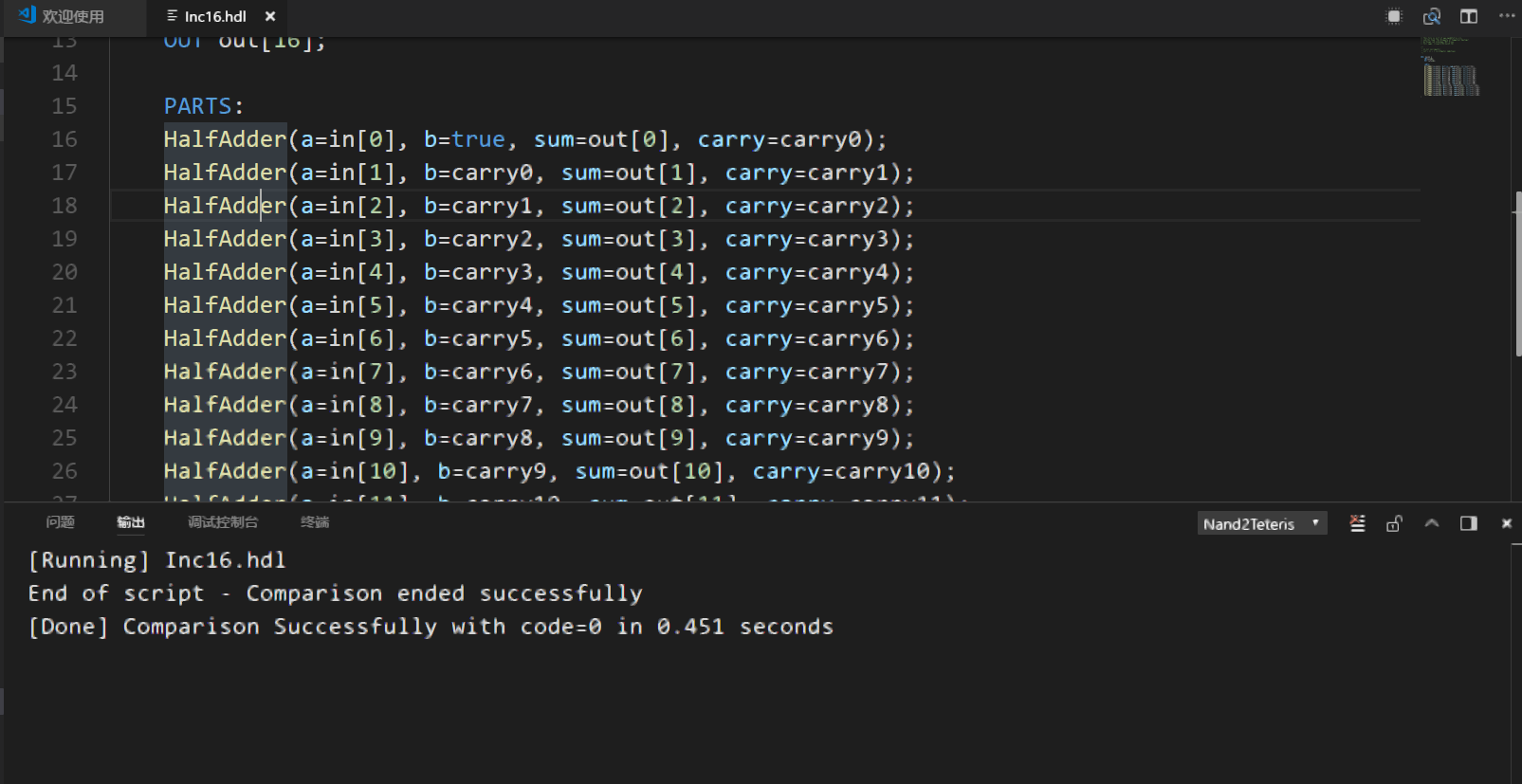
增量器
增量器是专门对指定数字加1的电路,书上说这样会带来很多便利
思路同上
算术逻辑单元 ALU
ALU的开发比较复杂,其核心思想是通过6个简单的控制位实现了16种计算
先按照预制指令顺序逐级处理,最后输出
遇到的问题是两个状态位zr,ng较难设计,我的思路是借助两个封装好的自写芯片IsNeg和Or16Way,因为内部总线不能单独取其中几位,zr ng可以选择性不设计
ALU的设计比较重要 请尽量不要参照下面的源码
ALU源码:
// This file is part of www.nand2tetris.org
// and the book "The Elements of Computing Systems"
// by Nisan and Schocken, MIT Press.
// File name: projects/02/ALU.hdl
/**
* The ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit).
* Computes one of the following functions:
* x+y, x-y, y-x, 0, 1, -1, x, y, -x, -y, !x, !y,
* x+1, y+1, x-1, y-1, x&y, x|y on two 16-bit inputs,
* according to 6 input bits denoted zx,nx,zy,ny,f,no.
* In addition, the ALU computes two 1-bit outputs:
* if the ALU output == 0, zr is set to 1; otherwise zr is set to 0;
* if the ALU output < 0, ng is set to 1; otherwise ng is set to 0.
*/
// Implementation: the ALU logic manipulates the x and y inputs
// and operates on the resulting values, as follows:
// if (zx == 1) set x = 0 // 16-bit constant
// if (nx == 1) set x = !x // bitwise not
// if (zy == 1) set y = 0 // 16-bit constant
// if (ny == 1) set y = !y // bitwise not
// if (f == 1) set out = x + y // integer 2's complement addition
// if (f == 0) set out = x & y // bitwise and
// if (no == 1) set out = !out // bitwise not
// if (out == 0) set zr = 1
// if (out < 0) set ng = 1
CHIP ALU {
IN
x[16], y[16], // 16-bit inputs
zx, // zero the x input?
nx, // negate the x input?
zy, // zero the y input?
ny, // negate the y input?
f, // compute out = x + y (if 1) or x & y (if 0)
no; // negate the out output?
OUT
out[16], // 16-bit output
zr, // 1 if (out == 0), 0 otherwise
ng; // 1 if (out < 0), 0 otherwise
PARTS:
// Put you code here:
//置0操作
Mux16(a=x, b=false, sel=zx, out=xzx);
Mux16(a=y, b=false, sel=zy, out=yzy);
//取反操作
Not16(in=xzx, out=xzxnx0);
Mux16(a=xzx, b=xzxnx0, sel=nx, out=xzxnx);
Not16(in=yzy, out=yzyny0);
Mux16(a=yzy, b=yzyny0, sel=ny, out=yzyny);
//并集操作
And16(a=xzxnx, b=yzyny, out=xzxnxANDyzyny);
//加法操作
Add16(a=xzxnx, b=yzyny, out=xzxnxADDyzyny);
//选择输出
Mux16(a=xzxnxANDyzyny, b=xzxnxADDyzyny, sel=f, out=ANDorADD);
//输出取反
Not16(in=ANDorADD, out=NotANDorADD);
//最终输出
Mux16(a=ANDorADD, b=NotANDorADD, sel=no, out=final);
Mux16(a=final, b=false, sel=false, out=out);
IsNag(in=final, out=ng);
Or16Way(in=final,out=nzr);
Not(in=nzr, out=zr);
}
CHIP Or16Way{
IN in[16];
OUT out;
PARTS:
Or8Way(in=in[0..7], out=o1);
Or8Way(in=in[8..15], out=o2);
Or(a=o1, b=o2, out=out);
}
CHIP IsNag {
IN in[16];
OUT out;
PARTS:
Mux(a=false, b=true, sel=in[15], out=out);
}
_(:3 」∠)_